Pipeline and research
Our vision for affordable personalized healthcare:
- Science, technology and Real World Data will ease the suffering from chronic diseases
- Smart wearables enable earlier diagnosis, better disease monitoring, and individualized intervention.
- Empowered patients and physicians engage in a more effective doctor-patient interaction
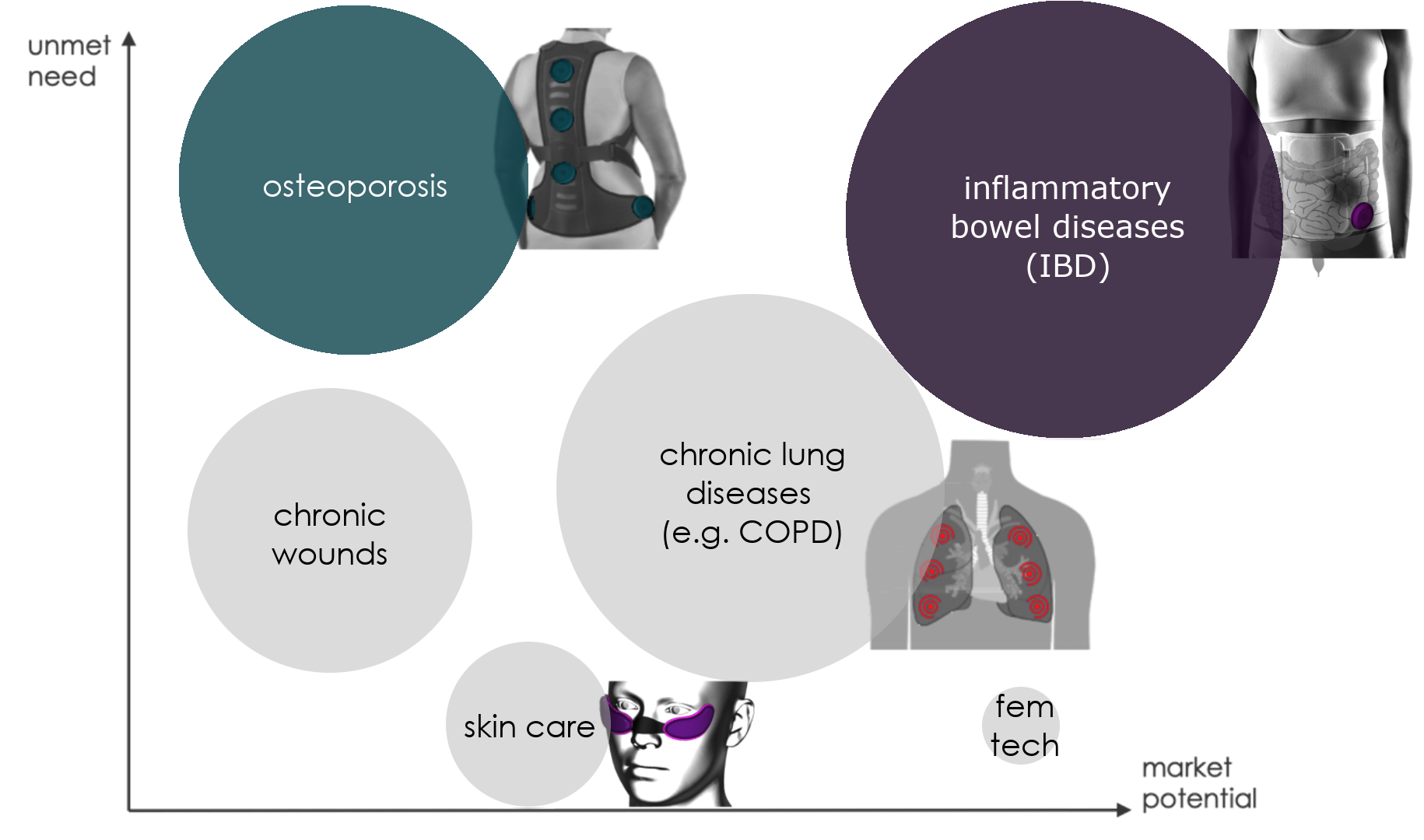
Based on research findings and technological capabilities, we consider the following monitoring and treatment goals. The medical needs are clearly defined and chronic in nature. In addition, current medications are often not suitable for long-term use.
We enjoy working with innovative research organizations, technology providers and life science companies to demonstrate the tangible benefits of new monitoring and therapeutic modalities.
Please reach out to us if you would like to to create future care solutions together with us.
Publications
- Linnemann, C.; Sahin, F.; Chen, Y.; Falldorf, K.; Ronniger, M.; Histing, T.; Nussler, A.K.; Ehnert, S. NET FormationWas Reduced via Exposure to Extremely Low-Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields. Int. J. Mol.Sci. 2023, 24, 14629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914629.
- Chen, Y.; Braun, B.J.; Menger, M.M.; Ronniger, M.; Falldorf, K.;Histing, T.; Nussler, A.K.; Ehnert, S. Intermittent Exposure to a 16 Hz Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Promotes Osteogenesis In Vitro through Activating Piezo 1-Induced Ca2+ Influx in Osteoprogenitor Cells. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14030165.
- Ronniger, M. et al; A Novel Method to Achieve Precision and Reproducibility in Exposure Parameters for Low-Frequency Pulsed Magnetic Fields in Human Cell Cultures, Bioengineering 2022, 9, 595; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100595.
- Chen Y. et al.; Modulation of macrophage activity by pulsed electromagnetic fields in the context of fracture healing, Bioengineering 2021, 8(11), 167; https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8110167.
- Chen Y. et al.; Exposure to 16 Hz Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Protect the Structural Integrity of Primary Cilia and Associated TGF- Signaling in Osteoprogenitor Cells Harmed by Cigarette Smoke, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7036; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137036.
- Ehnert S. et al.; Translational Insights into Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (ELF-PEMFs) for Bone Regeneration after Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery., J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 20;8(12):2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122028.
- Ziegler, P.N. et al.; Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy improves osseous consolidation after high tibial osteotomy in elderly patients., J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2008; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112008.
- Poh PSP et al.; Osteogenic Effect and Cell Signaling Activation of Extremely Low-Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells., Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 12;2018:5402853. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5402853.
- Ehnert S. et al.; Co-Culture with Human Osteoblasts and Exposure to Extremely Low Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Improve Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells., Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 27;19(4):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040994.
- Portelli L.A. et al.; Retrospective estimation of the electric and magnetic field exposure conditions in in vitro experimental reports reveal considerable potential for uncertainty, Bioelectromagnetics. 2018 Apr;39(3):231-243. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.22099.
- Ehnert S. et al.; Extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields cause antioxidative defense mechanisms in human osteoblasts via induction of •O2- and H2O2., Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 6;7(1):14544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14983-9.
- Ehnert S. et al.; Primary human osteoblasts with reduced alkaline phosphatase and matrix mineralization baseline capacity are responsive to extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic field exposure — Clinical implication possible., Bone Rep. 2015 Aug 18;3:48-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bonr.2015.08.002.
- Seeliger C et al.; Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields significantly improve time of closure and proliferation of human tendon fibroblasts., Eur J Med Res. 2014 Jul 5;19(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-783X-19-37.
- Visan A; Effective acceleration of wound healing processes with the help of Cell Information Therapy (CIT) – Innovation from quantum physics., January 2008 Kosmetische Medizin 29(1):23-27.
- Visan A; Efficacy and tolerance of cell information therapy (CIT) on wound healing processes free of transplants., January 2007 Kosmetische Medizin 28(3):112-118.


Siegfried Weller Institute for Traumatology Research
Topic:
Influence of CIT-technology on primary osteoblasts


Institut De Biologie Paris Seine (IBPS)
Topic:
Alleviation of Inflammation by physical (EMF + light) therapy

Mittelstand 4.0 Centre of Excellence Kiel
Topic:
Development of a wireless interface for use in a medical device environment

University of Southern Denmark
Topic:
Analysis of value proposition and patient journey regarding EMF therapy

Medical applications
Topic:
Influence of CIT-technology on the regeneration of cell cultures damaged through oxidative stress

AG Immune regulation
Topics:
- Influence of CIT-technology on the activation status and cytokine secretion of murine CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocytes
- Influence of CIT-technology on the signal transduction after TCR stimulation in human T-cell lines
Department of Applied Cell Therapy
Topic:
Influence of CIT-technology on the differentiation and function of immune oppressive macrophage populations
Computer Science VII
Topic:
Ontology based analysis and visualisation of the induced morphological changes of cells through CIT

Clinic and Polyclinic for Trauma Surgery and experimental Trauma Surgery
Topic:
Influence of CIT-technology on the osteogenic differentiation of stem cells for bone regeneration
Member of:

